Lecture 6: Asynchronous programming
By default, C# code is run in a synchronous way or on a single thread. This means that each line of code is executed one at a time in a sequential manner. The execution of one line is blocking for the subsequent line. By default only one thread, which is the smallest sequence of programmed instructions that the OS will allocate processor time.
The idea behind asynchronous programing is to let the execution continue even if one particular step is taking time.
The idea behind multithreading is to use multiple threads to execute computationally intensive code in parallel.
Multithreading
When using multithreading, multiple code units that are running independently.
- Ideal for computationally intensive applications (“CPU bound operations”)
- Makes use of the processing powers of modern CPUs.
- Example of applications: Image Analysis, Video games, web servers
| Figure1: Single-threaded Programming |
|---|
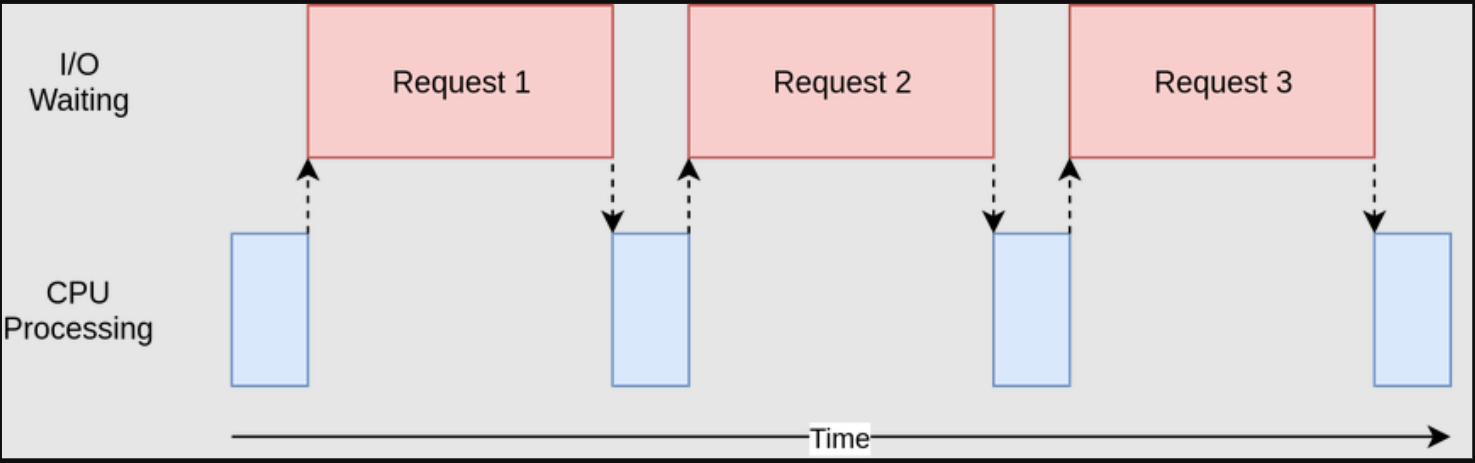 |
| Figure2: Multi-threaded Programming |
|---|
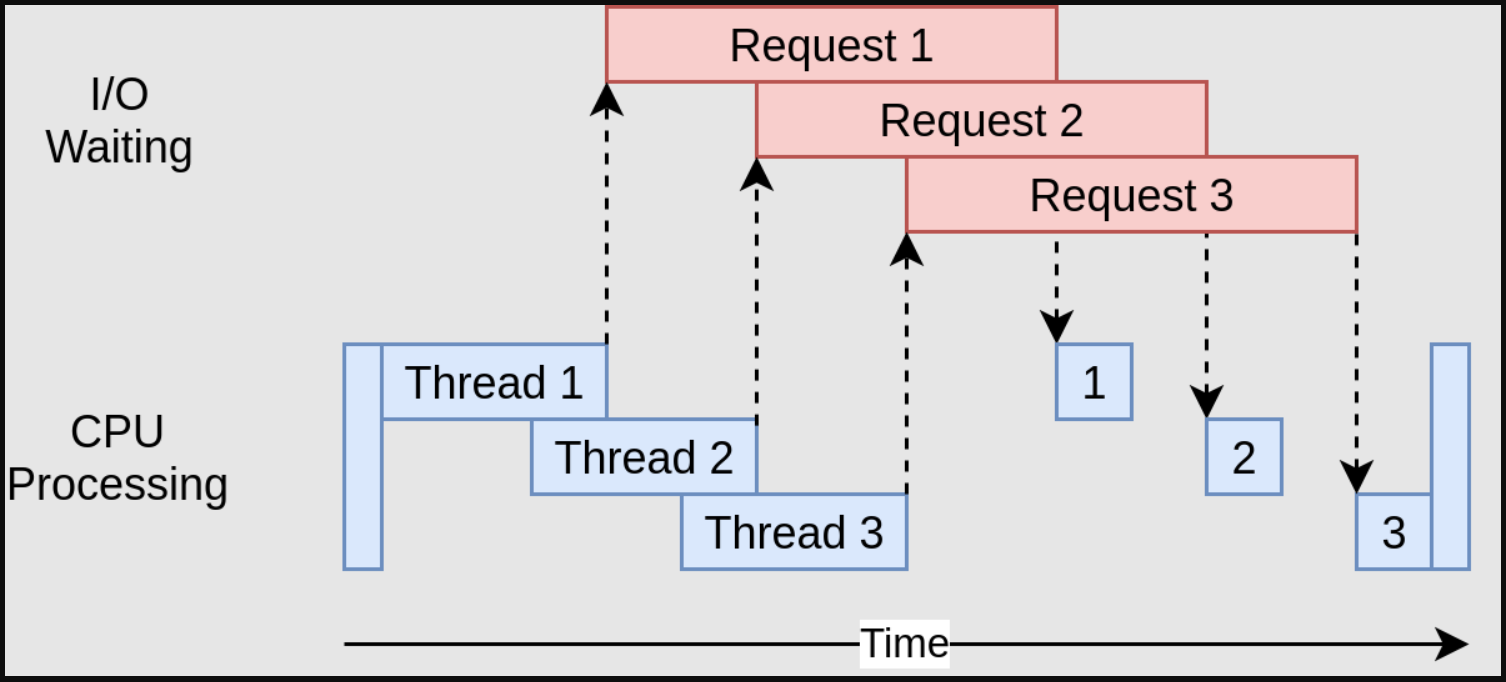 |
Asynchronous Programming
-
Asynchrony indicates that two or more processes are able to operate independently, and in some cases simultaneously, without any constraints on the relative timing of their execution.
-
Asynchronous programming is a programming paradigm that allows for the execution of multiple
taskssimultaneously.- The paradigm is particularly important in client-server architectures.
-
This enables programmers to write parallel code, which can take advantage of multiple processors or processor cores.
| Figure1: Synchronous Programming |
|---|
 |
- This enables programmers to write parallel code, which can take advantage of multiple processors or processor cores.
| Figure1: Asynchronous Programming |
|---|
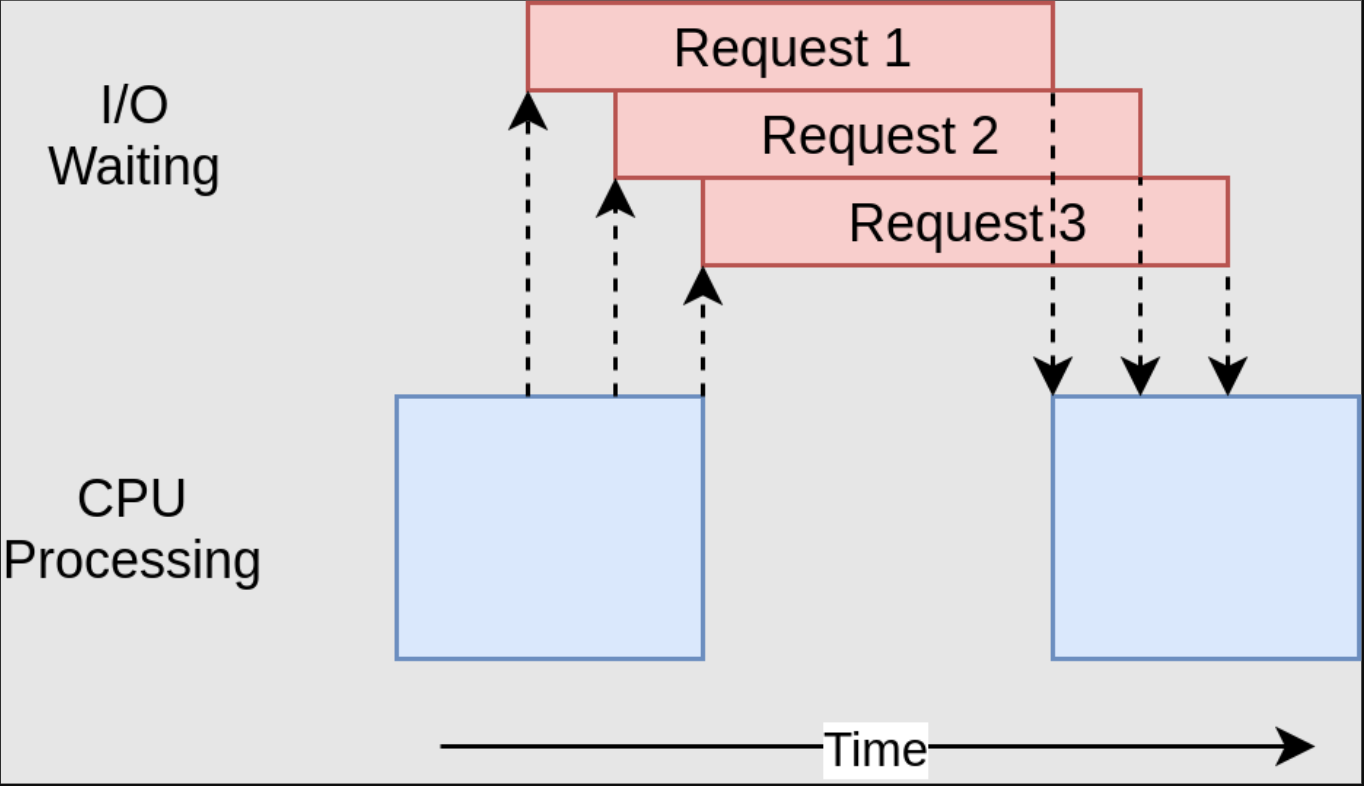 |
When to use Async programming over multi-threading?
If the app is waiting for a value because of a I/O-bound operation, a value to from a webserver, filesystem or a database, then there is no need for a dedicated thread to sit around and wait for the data when it can be servicing other requests.
-
Creating threads in a program is often undesirable.
-
Threads are the most low-level constructs of multithreading and working with them could be challenging and creates an overhead.
-
It is much more expensive to create a thread than re-using an existing thread from the thread pool.
Demo: BakingACakeAsync
One major difference between synchronous and asynchronous function calls is the nature of blocking threads. Let’s take the example of baking a cake in roughly 4 steps
- Gathering the ingredients
- Heating the oven
- Mixing the ingredients,
- Baking the cake.
namespace DemoAsync
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
BakingCakeSynchronously();
}
static void BakingCakeSynchronously()
{
var ingredients = GatherIngredients();
MixIngredients(ingredients);
HeatOven(250);
BakingCake(30);
CoolingCake(15);
}
// The rest of the code is in the Demos code repo
Now each one of those steps is going to take time although conceptually, we do not need to wait until all ingredients are gathered before starting to heat up the oven, nor do we need to wait until the oven is heated up to start mixing the ingredients. The problem with synchronous programing is the blocking nature of each execution. The complete code can be found in the Demos.
Now there’s multiple ways of improving the efficiency of this code. Let’s firstly explore asynchronous programing, which allows the execution of some functions to be non-blocking of the main thread, so for example starting to heat up the oven, then moving up to the next step of mixing the ingredients while waiting for the oven to finish heating up. It’s important to understand that it’s still single-threaded.
Task Class and async and await Keywords
The Class Task and/or Task<T> were introduced in .NET to wrap any method into a unified interface that is useful for the method caller to monitor the completion of whatever operation the method was intended to do. What’s essential to understand is that from the point of view of the caller, a task is giving us a “promise” of a variable but it won’t have control over how and when the execution is completed.
-
A
Taskis a future or a promise of value.- A
Task<T>promises to return you aTvalue, but not right away.
- A
-
A
Taskis a higher level abstraction- Capable of returning a value.
- Compositional in nature.
- Can use continuations and chain any amount of tasks together.
- Very useful for I/O bound operations.
-
Tasks provides error handling
- Each
Taskonce completed will have a state:- Ran to Completion
- Canceled
- Faulted.
- Uses
AggregateExceptionto wrap up any other exception that might occur.AggregateExceptionprovides a Flatten method to check all exceptions.
- Each
The async and await keywords were created in C# to makes creating asynchronous code almost as easily as you create synchronous code. You can use resources in .NET framework in the same exact way.
asyncandawaitkeywords were introduced in version 5 of C# (2012).- The
asynckeyword is used with method definitions and indicates an asynchronous method. - The
awaitkeyword is used with method class and suspends a method until the awaited asynchronous operation is completed.
Going back to our cake, the asynchronous method of baking a cake would have the following signature:
namespace DemoAsync
{
internal class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
await BakingCakeAsynchronously();
}
static async Task BakingCakeAsynchronously()
{
var ingredientsTask = GatherIngredientsAsync();
Task ovenTask = HeatOvenAsync(250);
var ingredients = await ingredientsTask;
var mixingTask = MixIngredientsAsync(ingredients);
await mixingTask;
await ovenTask;
await BakingCakeAsync(30);
await CoolingCakeAsync(15);
Console.WriteLine("Baking async completed");
await Task.Delay(1000);
}
static void BakingCakeSynchronously()
{
var ingredients = GatherIngredients();
MixIngredients(ingredients);
HeatOven(250);
BakingCake(30);
CoolingCake(15);
}
Example of HttpClients
The async and await keywords makes creating asynchronous code almost as easily as you create synchronous code. You can use resources in .NET framework in the same exact way. Here’s an example from Microsoft, that we will focus on:
public async Task<int> GetUrlContentLengthAsync()
{
var client = new HttpClient();
/*
GetStringAsync is an asynchronous methed to get a string value from the provided URL.
The value will be provided sometime in the future. Any reserved resouces will be released
continue processing.
*/
Task<string> getStringTask = client.GetStringAsync("https://docs.microsoft.com/dotnet");
FinishOtherOperations();
/*
This is the future time in my program where I will need to wait for the my promised values.
Suspends a thread until a specific operation is completed
*/
string contents = await getStringTask;
return contents.Length;
}
private void FinishOtherOperations()
{
Console.WriteLine("Working...");
}
Check this great article on asynchronous programming in .NET: 10 Best Practices in Async-Await Code in C# .
Sources
[1] Speed up your python program with concurrency
[3] Threading in C#